In this article, we’ll learn what are Excel file formats and extensions, and what distinguishes one from another. We’ll also see how to know the type of an Excel file and how to change it to another format when needed.
A/ Excel file formats and extensions
Excel has many different file formats or types that are distinguished by their extensions, and each file type has its purpose that makes it more useful for some tasks and situations than for others.
In the following table, I have listed the Excel file formats and extensions, along with a description of their purpose and characteristics.
| Format/Type | Extension | Description and Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Excel workbook (versions 2007 and later) | .xlsx | – Default Excel file for Excel 2007 and newer, based on the Office Open XML format. – Cannot store VBA macro code (to do that, you’ll need to use the dedicated format .xlsm). |
| Excel 97-2003 workbook | .xls | – Default Excel file for Excel 2003 and earlier, based on the Microsoft Binary Interchange File Format (BIFF8). – Unlike the .xlsx format, this file type can store VBA macro code. |
| Excel macro-enabled workbook (versions 2007 and later) | .xlsm | Excel workbook with macros for versions 2007 and newer (stores VBA macro code). |
| Excel macro-enabled workbook (2003 and earlier) | .xlm | Excel workbook with macros for versions 2003 and earlier (stores VBA macro code). |
| Excel binary workbook (versions 2007 and later) | .xlsb | – Default Excel binary workbook that uses the Microsoft Binary Interchange File Format (BIFF12) in Excel 2007 and newer. – Faster than .xlsx format – Can contain macros. |
| Excel template (versions 2007 and later) | .xltx | – Excel template for versions 2007 and newer. – A template is used as a strating point for creating new workbooks that will have the same layout, formatting, graphics, formulas, etc, without the need to recreate these aspects each time. – Cannot contain macros. |
| Excel template (versions 2003 and earlier) | .xlt | – Excel template for versions 2003 and earlier. – A template is used as a strating point to create new workbooks without the need to recreate each time the same layout, formatting, graphics, formulas, etc. – Can contain macros. |
| Excel macro-enabled template (versions 2007 and later) | .xltm | – Excel template with macros for versions 2007 and newer. – Unlike the .xltx, this template format stores VBA macro code. |
| Excel add-in (versions 2007 and later) | .xlam | Excel add-in with macros for versions 2007 and newer (stores VBA macro code). |
| Excel add-in (versions 2003 and earlier) | .xla | Excel add-in with macros for versions 2003 and earlier. |
Now that we know the main Excel file formats and their extensions, let’s see how you could know which format is your Excel file and which extension it has, as well as how to change this format and extension (or if you want, how to convert an Excel file from one format to another).
B/ How to know the Excel file format and extension
If you don’t have the extensions displayed for your files in Windows, you still can know which format and extension they have.
To know the format of an Excel file and the extension:
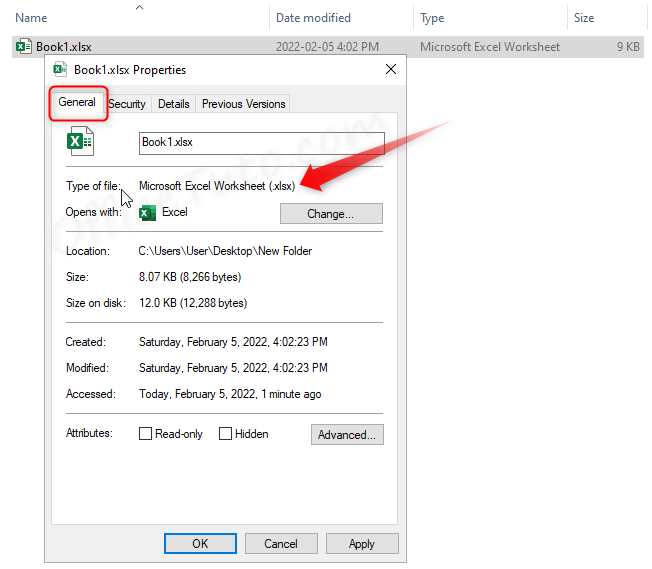
- Right-click on the name of the Excel file.
- At the bottom of the list, click on “Properties”.
- “Properties” window opens in its “General” tab.
- “File Type” section shows the type and extension.
C/ How to change Excel file format and extension
You would need to change the type of an Excel file:
- If you’re using it for an app that requires a different type.
- or if you want to benefit from a characteristic that the current type doesn’t have and that is present in another type; for example, the support of macros (from xlsx to xlsm), or less weight (from xls to xlsx), or more speed (from xlsx to xlsb)…
To change your Excel file type/format (and extension):
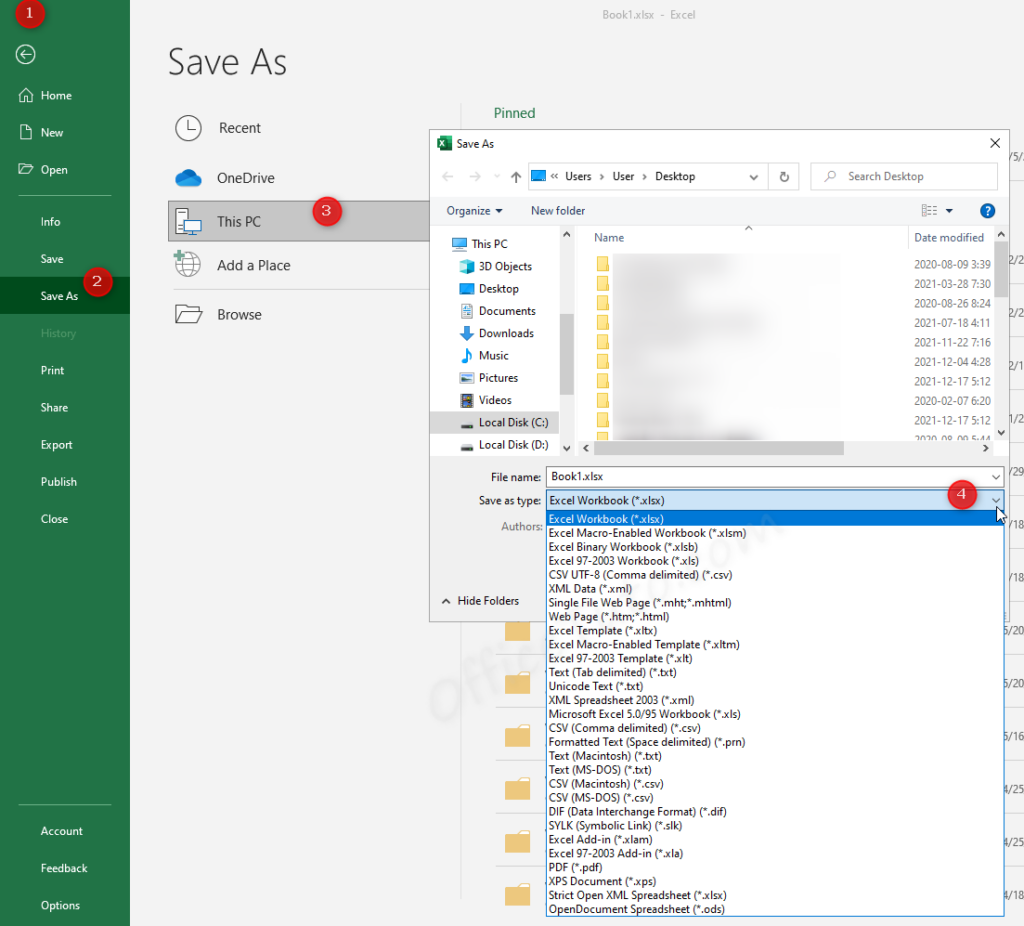
- Click on File tab (Office button in Excel 2007).
- Click on “Save As”.
- Choose where you want to save your file.
- The “Save As” dialog box displays.
- Click on the drop-down “Save as type”.
- Choose the file format and extension you want.
- Finally, click on “Save”.
- The file has now the new format and extension.
Note that you can change your Excel file format and extension in Windows directly from the name file, by changing the extension while renaming it, if you have allowed the display of the file extensions in your system.
In the following, I will show you how to display the file name extensions in Windows 7, 10, and 11.
– Display the file name extensions in Windows 7
- Open any folder.
- In the top blue bar, click on “Organize”.
- Then, click on “Folder and search options”.
- The “Folder Options” dialog box displays.
- Click on the “View” tab of this dialog box.
- Go to the “Advanced Settings” section.
- Uncheck “Hide extensions for known file types”.
- Click “OK”.
– Display the file name extensions in Windows 10
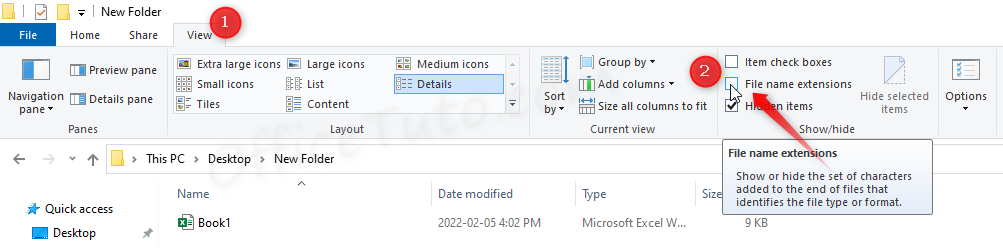
- In any folder, click on the “View” tab.
- Check “File name extensions” checkbox.
You can also use the “Folder Options” dialog box to show the file name extensions in Windows 10, but I preferred to show you the fastest and easiest method.
– Display the file name extensions in Windows 11
- Open any folder.
- Click on the three dots … of the menu bar.
- Click on “Options”.
- The “Folder Options” dialog box displays.
- Click on the “View” tab of this dialog box.
- Go to the “Advanced Settings” section.
- Uncheck “Hide extensions for known file types”.
- Click “OK”.
D/ Wrap up
So, that was the article about Excel file formats, where I gave you a list of the main Excel files, along with their extensions and a description of their purpose. I also showed you how to know which type is your Excel file and what extension it has, as well as how to change the format (and extension) of an Excel file and when you’ll need to do it.

